5.2.3 Priority of authentication when Layer 2 authentication is used together
- <Structure of this section>
(1) Prioritizing authentication when IEEE802.1X coexists with Web authentication or MAC authentication
If you do not perform multi-step authentication, IEEE802.1X static VLAN takes precedence over Web and MAC authentication. Note that IEEE802.1X dynamic VLAN mode has the same priority as Web authentication and MAC authentication, and retains the authentication result of the authentication function that was previously authenticated successfully. Authentication-first operation for IEEE802.1X fixed VLAN is described below.
If authentication using IEEE802.1X's fixed VLAN mode is successful after successful Web authentication or MAC authentication on the same terminal (a terminal with the same MAC address), the authentication result of IEEE802.1X is prioritized and the authentication status of Web authentication or MAC authentication is canceled (in Web authentication, the logout window is not displayed).
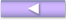
Note that IEEE802.1X authentication is not automatically canceled when the authenticated terminal of MAC authentication or Web authentication moves to the port. For example, if a terminal connected through a HUB (HUB#1 in the figure below) connected to a different port is already authenticated by IEEE802.1X (terminal authentication mode) and the connection is changed to a different HUB (HUB#2 in the figure below), you cannot log in to Web authentication (fixed VLAN mode) or MAC authentication (fixed VLAN mode) once IEEE802.1X authentication has not been canceled. To do so, use the clear dot1x auth-state command.
|
|
(2) Prioritizing authentication when Web authentication and MAC authentication coexist
If multi-step authentication is not performed and MAC authentication succeeds first on the same terminal (terminal with the same MAC address), Web authentication will result in an authentication error. Similarly, if a Web-authenticated terminal subsequently attempts MAC-based authentication, the authentication process will end in an error and the Web authentication status will remain in effect.



![[Figure Data]](./GRAPHICS/ZU250040.GIF)