26.1.2 Basic operation of VXLAN
When a VXLAN frame is received, the Switch learns the following at VTEP set for the Switch:
-
Source MAC address
-
Source IP address
-
Source VNI
Then, the forwarding bandwidth through the Layer 3 network is reduced by forwarding Layer 2 frames based on the learned information.
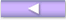
The following figure shows the basic operation of VXLAN when ARP request frame and ARP response frame are forwarded. In this diagram, Switch 1, Switch 2, and Switch 3 have the same VNI ID of VXLAN tunneling.
|
|
-
A ARP is requested (broadcast frame) from Host1.
-
Switch 1 encapsulates (adds VNI) the received ARP requestI will. VXLAN tunneling is used to unicast to Switch 2 and Switch 3 in the same VNI.
-
Switch 2 registers the learned information from the received VXLAN frame in MAC address table.
-
Switch 2 decapsulates (VNI deletes) VXLAN frame and forwards ARP request frame to Host2.
-
ARP replies are received from Host2.
-
Switch 2 encapsulates (adds VNI to) the received ARP reply. Because the destination has been learned, it is unicast to Switch 1 using VXLAN tunneling.
-
Switch 1 registers the learned information from the received VXLAN frame in MAC address table.
-
Switch 1 decapsulates (VNI deletes) VXLAN frames and forwards ARP reply frame to Host1.



![[Figure Data]](./GRAPHICS/Z6152020.GIF)